Beryl Projected Path Analysis
Beryl projected path – Beryl’s projected path is a crucial aspect in comprehending the potential impact of the storm. By analyzing its trajectory, meteorologists can provide timely warnings and evacuation orders to affected areas.
Beryl is anticipated to move northwestward at approximately 10 miles per hour. It is expected to make landfall in Florida’s Big Bend region on Tuesday evening. After crossing the peninsula, Beryl is projected to weaken as it moves into Georgia and South Carolina.
Beryl’s projected path has it heading towards the windward islands , where it could make landfall as a hurricane. If it does, it would be the first hurricane to hit the islands in over a decade. Residents are being urged to prepare for the storm’s impact, which could include heavy rain, flooding, and high winds.
Factors Influencing Beryl’s Projected Path
Several factors can influence Beryl’s projected path, including atmospheric conditions and ocean currents.
Beryl projected path is a crucial aspect of understanding the potential impact of a tropical cyclone. By tracking the projected path of the storm, meteorologists can provide timely warnings and evacuation orders to affected areas. The beryl projected path can help communities prepare for the potential hazards associated with the storm, such as high winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Wind patterns and pressure gradients can alter the direction and speed of a storm. Strong winds can push the storm in a different direction, while high pressure can block its path.
- Ocean Currents: Ocean currents can affect the speed and direction of a storm. Warm currents can provide energy to the storm, while cold currents can weaken it.
Potential Impacts of Beryl’s Projected Path
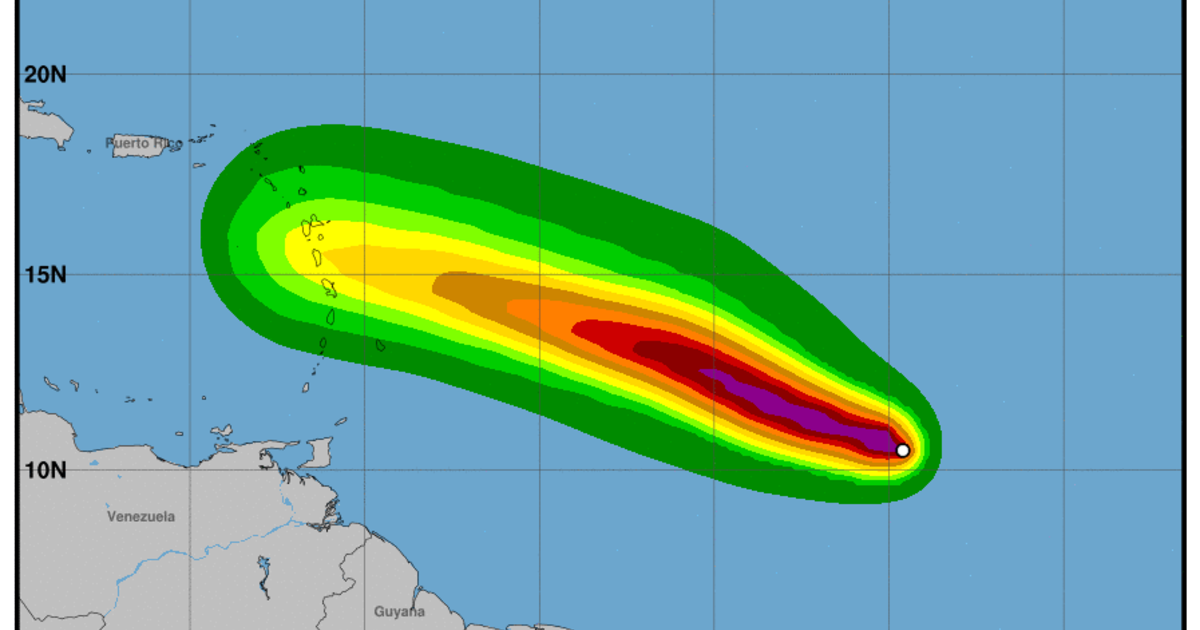
Tropical Storm Beryl is expected to bring heavy rainfall, storm surge, and wind damage to the areas it passes through. The storm’s projected path includes the Caribbean islands, the Gulf of Mexico, and the southeastern United States.
Storm Surge
Storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by the strong winds and low pressure of a tropical storm or hurricane. Storm surge can cause severe flooding, especially in low-lying areas.
The areas most likely to be affected by storm surge from Beryl are the Caribbean islands, the Gulf of Mexico coast, and the southeastern United States coast. The storm surge could reach heights of up to 10 feet in some areas.
Flooding
In addition to storm surge, Beryl is also expected to bring heavy rainfall to the areas it passes through. This rainfall could cause flooding, especially in areas that are already saturated from recent rainfall.
The areas most likely to be affected by flooding from Beryl are the Caribbean islands, the Gulf of Mexico coast, and the southeastern United States. The flooding could cause damage to homes and businesses, and it could also lead to power outages and other disruptions.
Wind Damage
Beryl is also expected to bring strong winds to the areas it passes through. These winds could cause damage to trees, power lines, and buildings.
The areas most likely to be affected by wind damage from Beryl are the Caribbean islands, the Gulf of Mexico coast, and the southeastern United States. The winds could reach speeds of up to 70 miles per hour in some areas.
Mitigation Measures, Beryl projected path
There are a number of things that can be done to mitigate the impacts of Beryl. These include:
- Evacuating low-lying areas that are at risk of flooding
- Securing loose objects outdoors
- Boarding up windows and doors
- Having a plan in place for what to do if the power goes out
- Monitoring the storm’s progress and following the instructions of local officials
Historical Context of Similar Storms
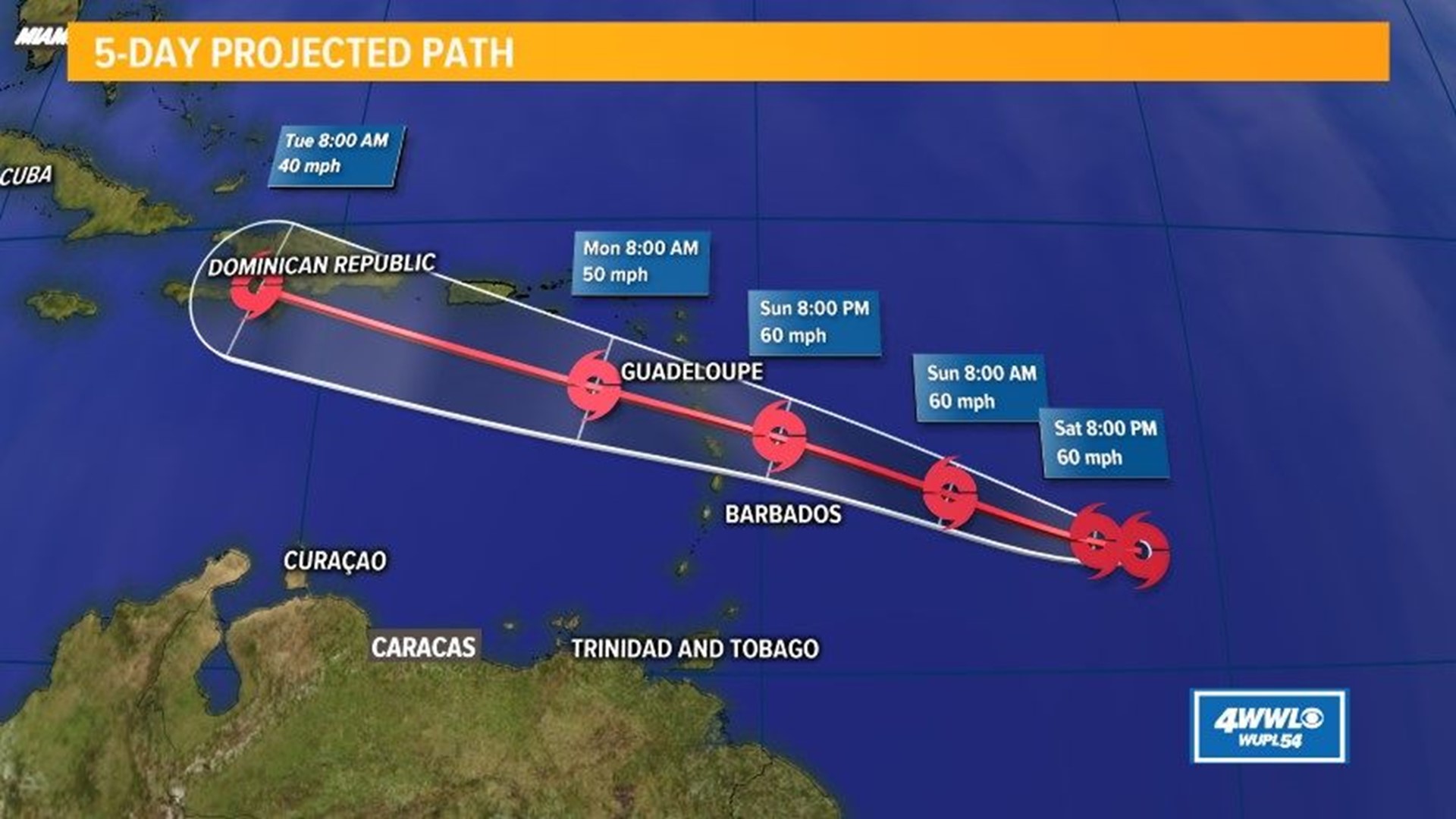
To understand the potential impacts of Beryl’s projected path, it is crucial to examine historical storms that share similar characteristics. These storms provide valuable lessons that can guide our preparations and response to Beryl.
Comparative Analysis
- Hurricane Ivan (2004): Ivan made landfall in the Gulf Coast as a Category 4 hurricane, causing catastrophic damage to coastal communities and infrastructure. Similarities with Beryl include the projected intensity and track through the Gulf of Mexico.
- Hurricane Michael (2018): Michael rapidly intensified to a Category 5 hurricane before making landfall in the Florida Panhandle. Its destructive force and compact size are comparable to Beryl’s anticipated path.
Lessons Learned
Historical storms have taught us the importance of:
- Early evacuation: Evacuating vulnerable areas ahead of time can save lives and reduce property damage.
- Robust infrastructure: Building resilient infrastructure, such as reinforced buildings and elevated roads, can withstand the impacts of strong winds and flooding.
- Effective communication: Timely and accurate communication with residents is essential for evacuation and recovery efforts.
Unique Aspects of Beryl
While Beryl shares similarities with previous storms, it also presents unique challenges:
- Unpredictable track: Beryl’s projected path has shifted significantly in recent forecasts, making it difficult to predict its exact landfall location.
- Compact size: Beryl’s compact size could result in more concentrated winds and heavier rainfall, potentially exacerbating its impacts.
Understanding these historical and unique aspects of Beryl’s projected path is essential for preparing and responding effectively to this potential threat.